When an organization wants funding, whether or not to launch a brand new product, develop operations, or simply keep afloat, it doesn’t simply decide a financing technique out of a hat.
There’s a pure order to it based mostly on a well-established concept, fairly than being a desire. Often called the pecking order concept, this capital construction mannequin explains how corporations rank funding sources based mostly on threat, price, and the way a lot outsiders must know.
What’s the pecking order concept?
The pecking order concept states that companies finance initiatives utilizing inside funds first, then debt, and problem fairness solely as a final resort. This hierarchy reduces signaling threat as a result of issuing fairness would possibly indicate overvaluation and reduce investor confidence.
Monetary evaluation software program and monetary threat administration software program play a big function in how corporations analyze their money movement and monetary economics to search out sources of financing. Myers and Majluf popularized the pecking order concept to assist companies make sound financing selections.
On this information, we’ll unpack the idea, present the way it works in observe, clarify its roots in uneven data, examine it to the trade-off concept, and discover how corporations use monetary software program to place these ideas into motion.
TL;DR: Every little thing you’ll want to find out about pecking order concept
- Why do corporations want utilizing inside funds first? As a result of it’s the most cost effective, least dangerous choice: no curiosity, no dilution, no outdoors scrutiny.
- When does debt make extra sense than fairness? Debt comes subsequent when inside funds run dry. It’s often cheaper than fairness and doesn’t dilute possession, although it provides compensation threat.
- Why is fairness thought-about a final resort? Issuing fairness can sign weak spot or overvaluation to traders, and it’s usually the costliest capital attributable to shareholder return expectations.
- What function does data asymmetry play in financing selections? Exterior traders know lower than insiders, which will increase perceived threat, and that drives up the price of debt and fairness.
- How can corporations select the very best financing supply? Through the use of monetary evaluation and threat modeling instruments to evaluate price, management, and timing, particularly when navigating unsure markets.
How does the pecking order concept affect capital construction?
Should you’re anticipating an organization to calculate some excellent debt-to-equity ratio and stick with it perpetually, that’s not how the actual world works. Based on the pecking order concept, most companies don’t begin with a great capital combine. As a substitute, they comply with a what’s obtainable and least painful method to funding.
Right here’s how the hierarchy performs out:
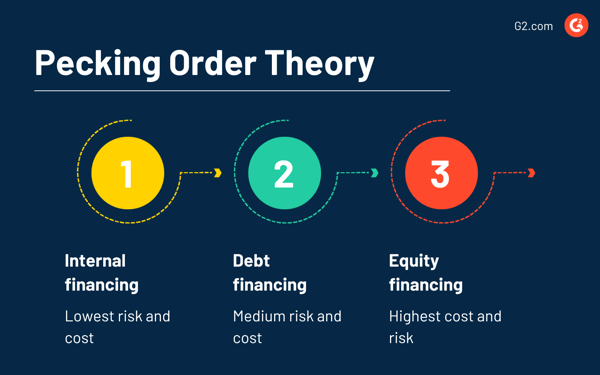
1. Retained earnings: Low-cost, simple, and yours
Each time doable, corporations want to make use of their very own earnings. It’s cost-free, doesn’t contain outdoors events, and retains management in-house. There’s no debt to repay, no fairness to dilute, and no monetary footnotes to clarify to shareholders. Retained earnings are the cleanest choice, which is why it is on the prime of the listing.
2. Debt financing: Helpful, however comes with strings
Debt financing is available in second due to the curiosity funds related to utilizing debt capital. Whether or not the corporate takes out enterprise loans or points company bonds, it should pay some curiosity, making the price of debt greater than the non-existent price of utilizing retained earnings.
Nonetheless, it’s typically the lesser evil in comparison with issuing new shares.
3. Fairness financing: Costliest, most dangerous
Fairness financing (issuing new inventory) is usually the final transfer, not as a result of it’s logistically arduous, however due to what it alerts. Buyers typically see share issuance as a telltale signal of a better share valuation than the market worth. They deal with this sign as an indicator of soon-to-drop share costs.
On prime of that, fairness is pricey. Buyers count on larger returns to compensate for threat, and current shareholders don’t love seeing their slice of the pie shrink. That’s why fairness financing often comes into play solely when inside and debt choices are maxed out, or strategically off the desk.
How does uneven data have an effect on the pecking order concept?
To actually get why corporations stick with a financing hierarchy, you’ll want to perceive the ability of data imbalance, or in additional technical phrases, uneven data. This occurs when insiders (like executives) have a clearer image of the corporate’s monetary well being, dangers, and future prospects than outsiders (like lenders or traders).
Now, not all financing strategies are affected equally by this data hole.
When an organization makes use of its funds, there’s no hole. Nobody wants convincing. It’s probably the most easy and least dangerous choice, as a result of the corporate is aware of precisely what it’s working with.
Debt introduces a bit extra complexity. Lenders don’t must know the whole lot in regards to the firm; they largely care whether or not the enterprise will pay them again, with curiosity. If the compensation threat is low and the financials take a look at, debt stays a comparatively reasonably priced choice.
However issues change dramatically with fairness. Fairness traders are placing their cash in with no assured return. They’re counting on restricted public data and need to belief administration’s outlook. As a result of they’re flying blind, they’ll demand larger returns to make up for the uncertainty, and that’s what drives up the price of fairness capital.
So when corporations comply with the pecking order, it’s not nearly frugality. It’s about minimizing the price of capital and avoiding market misunderstandings. The extra unsure the surface world is about your monetary state of affairs, the extra you’ll need to pay to persuade them you’re well worth the threat.
Instance of making use of the pecking order concept to a real-world determination
Think about you are the CFO of a mid-sized firm with an thrilling alternative on the desk: a brand new challenge that would gasoline long-term development. The catch? You’ll want $15,000 to get it off the bottom. So, the place ought to the cash come from?
Choice 1: You examine the books. Excellent news: the corporate has sufficient retained earnings to totally cowl it. That’s the best state of affairs. You don’t must borrow from a financial institution, dilute possession, or clarify something to traders. Simply allocate the funds and go. Clear, easy, and 0 friction.
Choice 2: However let’s say retained earnings are already tied up elsewhere. Your subsequent transfer? Tackle debt. You method a lender and get authorized for a short-term mortgage at 5% curiosity. That’s $750 in financing price ($15,750 in complete) — not nothing, however manageable. You protect possession and ship no crimson flags to the market. In fact, there’s compensation strain now, and the mortgage impacts your debt-to-equity ratio, nevertheless it’s nonetheless a standard and comparatively low-cost transfer.
Choice 3: As a CFO, you would possibly conclude that debt financing isn’t very best as a result of lenders don’t have the debt capability, otherwise you aren’t positive your organization could have sufficient web debt after paying the cash it borrows.
You might also wish to enhance the corporate’s debt ratios. Higher to catch these debt points beforehand; you would not wish to go bankrupt! Now, you should utilize fairness financing and problem fairness to get that $15,000 you want.
If your organization’s inventory value is $30 per share, you’d must promote 500 shares to achieve $15,000 in debt capital. Nonetheless, this decreases your share value by, as an instance, $2 per share, making every share price $28. Which means you are giving up an additional $2 per share (or $1,000 complete) whenever you promote these 500 shares.
You’ll get the $15,000 immediately, however find yourself paying extra dividends ($16,000 in complete) when factoring in the price of new fairness.
Pecking order concept vs. trade-off concept: what’s the distinction?
Not each firm follows the identical logic when deciding find out how to finance development, and that’s the place the trade-off concept enters the dialogue.
Whereas the pecking order concept explains how corporations are likely to behave (based mostly on entry to data and signaling considerations), the trade-off concept is extra of a prescriptive mannequin. It says an organization ought to intention for an optimum capital construction: balancing the advantages of debt (like tax financial savings) towards the dangers (like chapter or monetary misery).
So which one’s proper?
Nicely, they’re not mutually unique. In reality, many companies begin by following the pecking order, and later refine their construction utilizing trade-off concept ideas as soon as they’re mature sufficient to mannequin threat and return exactly.
Right here’s how the 2 examine:
| Issue | Pecking order concept | Commerce-off concept |
| Core thought | Reduce financing friction | Optimize capital combine |
| Key driver | Uneven data | Stability the tax advantage of debt vs. the price of misery |
| Habits model | Reactive and preference-based | Strategic and target-based |
| Works greatest for | Startups, personal companies, and unsure markets | Mature corporations with secure earnings |
| Key limitation | No “optimum” ratio, only a hierarchy | Assumes corporations can quantify threat completely |
In easy phrases, the pecking order reveals how corporations are likely to act, whereas trade-off concept suggests how they need to act, assuming they’ve received the information and threat tolerance to again it up.
When ought to an organization deviate from the pecking order concept?
The pecking order concept is a great default, however not a tough rule. In some circumstances, flipping the script on the same old funding order can truly be the higher transfer.
Right here’s when that is sensible:
- Fairness is unusually low cost: In case your valuation is excessive and the market is bullish, issuing fairness early can elevate extra capital with much less dilution. In some circumstances, that’s cheaper than taking over debt.
- Debt is strategically preferable: Low rates of interest and tax-deductible curiosity could make debt extra enticing than utilizing up inside funds, particularly if you wish to protect liquidity.
- Fairness brings greater than money: Typically traders supply strategic worth: partnerships, distribution channels, or board-level experience. In these circumstances, fairness turns into an asset, not only a price.
What are the professionals and cons of the pecking order concept?
Like all monetary framework, the pecking order concept isn’t flawless. Listed here are a few of its benefits and drawbacks.
Benefits of the pecking order concept
Right here’s the place the pecking order concept gives clear strategic worth for finance groups and decision-makers.
- It displays real-world decision-making. The idea acknowledges that the majority corporations want utilizing inside funds earlier than taking over threat or dropping management, one thing conventional capital construction fashions typically overlook.
- It promotes capital self-discipline. By encouraging corporations to prioritize retained earnings, the idea minimizes pointless dilution and over-leveraging.
- It accounts for signaling threat. Each financing transfer sends a message. Issuing fairness can set off investor suspicion. The pecking order helps companies decrease these market alerts till they’re unavoidable.
- It’s particularly helpful for startups and personal companies. The place data asymmetry is excessive and entry to capital is restricted, this hierarchy is commonly adopted intuitively.
Limitations of the pecking order concept
For all its readability, the mannequin misses some vital nuances that matter in trendy finance.
- It ignores hybrid financing choices. Devices like convertible notes or most well-liked fairness don’t neatly match into the interior → debt → fairness ladder, but they’re frequent in trendy finance.
- It doesn’t account for market timing. An organization would possibly select fairness first throughout favorable circumstances, even when it nonetheless has inside funds, to capitalize on a robust valuation.
- It lacks a quantitative framework. The idea reveals desire, not optimization. It received’t inform you your very best debt-to-equity combine or how a lot retained earnings to reinvest.
- It assumes capital availability follows logic. In observe, entry to debt or fairness typically will depend on investor sentiment, financial cycles, or relationship historical past, not simply inside preferences.
Instruments for utilizing the pecking order concept
The pecking order concept can solely be used whenever you perceive an organization’s funds. Gathering and analyzing monetary information will be annoying with out the suitable instrument. G2 helps corporations discover monetary evaluation and threat administration options to trace, handle, and analyze funds.
Monetary evaluation software program options
Monetary evaluation instruments assist corporations monitor monetary efficiency. These options collect and analyze monetary transactions and accounting information that can assist you keep on prime of key efficiency indicators (KPIs) and make sensible monetary selections. Accountants additionally use these methods for report technology and monetary compliance functions.
Monetary threat administration software program options
Monetary threat administration methods support monetary companies establishments in recognizing and mitigating funding dangers. These instruments play a key function in how corporations simulate funding eventualities, conduct in-depth analyses, and discover appropriate funding alternatives.
Incessantly requested questions on pecking order concept
Acquired extra questions? We’ve got the solutions.
Q1. What precisely does the pecking order concept assume?
It assumes corporations want to fund themselves utilizing inside money first, then debt, and solely flip to fairness as a final resort. The mannequin displays how companies rank funding sources based mostly on price, management, and threat.
Q2. Why does uneven data matter a lot?
As a result of it creates threat for traders, when outsiders know lower than firm insiders, they demand the next return, particularly for fairness. That’s what makes exterior capital dearer.
Q3. Is that this concept nonetheless helpful in at this time’s market?
Completely, notably for startups, personal companies, and corporations in unsure markets. It’s typically used alongside different fashions like trade-off concept or market timing concept to kind a extra full funding technique.
This autumn. What’s the distinction between the pecking order and trade-off concept?
Pecking order is about behavioral desire: inside funds first, fairness final. Commerce-off concept is extra quantitative, aiming for the best debt-equity combine by balancing tax benefits with chapter threat.
Q5. Can the pecking order concept be utilized to startups?
Sure, however typically in reverse. Startups often lack inside funds or credit score historical past, so that they elevate fairness first, usually by angels or VCs, not as a result of it’s very best, however as a result of it’s accessible.
Make good monetary selections
The pecking order concept explains how and why corporations select between inside financing, debt, and fairness to finance their companies. The idea doesn’t information decision-making regardless of its usefulness in monetary administration based mostly on capital construction selections.
Plus, there’s no quantitative metric that reveals you find out how to analyze or calculate financing sources. Think about using the pecking order concept with different instruments to drive sound capital market selections.
Leverage best-in-breed monetary predictive analytics software program options to drive funding technique with historic information evaluation.
This text was initially revealed in 2019. It has been up to date with new data.

