Builders and designers spend their days juggling stay deployments, debugging integrations, and retaining IT programs buzzing.
However within the midst of all this complexity, the invisible layer connecting all of it, the message dealer, typically goes unnoticed. Finally, it results in knowledge silos, manufacturing fatigue, and fault isolation.
With a message dealer, you may automate communication and message supply between two or extra programs to electronically change essential deliverables. To make sure a seamless switch of knowledge, builders use message queue software program, which acts as an middleman between the sender system and the receiving system.
What’s a message dealer?
A message dealer is software program that routes messages between functions, providers, or programs. It permits communication throughout totally different platforms or protocols by translating and relaying knowledge. Message brokers decouple providers, enhance scalability, and guarantee dependable message supply in distributed architectures.
Message brokers are included in messaging middleware or message-oriented middleware (MOM) programs. This type of middleware offers builders a constant method to dealing with knowledge circulation amongst an utility’s parts and focuses on its core performance.
TL;DR: Every part it is advisable to learn about message brokers
- What it’s: A message dealer is middleware software program that permits communication between functions, programs, and providers by routing, translating, and queuing messages asynchronously.
- Why do you want it? Message brokers decouple providers, enhance fault tolerance, assist async workflows, and allow scalable, event-driven or microservices-based architectures.
- What are the varieties of message brokers? Level-to-point (queue-based), publish/subscribe (topic-based), and hybrid messaging fashions that mix sturdiness with broad distribution.
- How do message brokers work? They obtain messages from producers, route them through exchanges or queues, and ship them to shoppers, thus dealing with retries, persistence, and translation alongside the way in which.
- The place can you utilize them? Fee programs, e-commerce success, IoT communication, real-time analytics, cloud-native apps, and hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- What are the very best message dealer instruments? RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka, Redis, Amazon SQS/SNS, Amazon MQ, and Apache ActiveMQ, every suited to particular scalability, throughput, or sturdiness wants.
Why use a message dealer?
As programs scale and develop into extra distributed, a message dealer helps simplify communication, cut back dependencies, and enhance service efficiency.
Right here’s how a message dealer helps:
- Decouples providers: As an alternative of providers calling one another immediately, they convey by the dealer. This enables every part to evolve independently, making programs simpler to construct, check, and preserve, particularly in microservices and event-driven architectures.
- Improves fault tolerance: If a downstream service is unavailable or overloaded, the dealer queues the message and retries supply when potential. This ensures messages aren’t misplaced and programs can get well gracefully from non permanent failures with out person affect.
- Helps cross-language or cross-platform integration: Message brokers act as protocol translators between programs constructed with totally different tech stacks. Providers may be written in several languages or hosted in several environments whereas nonetheless speaking seamlessly utilizing commonplace message codecs.
- Allows horizontal scalability: By distributing messages throughout a number of client cases, brokers make it simple to scale out providers with out rewriting enterprise logic. This load balancing functionality is essential for dealing with high-throughput or bursty site visitors.
- Integrates throughout hybrid and multi-cloud environments: Brokers can bridge on-prem programs, public clouds, and edge units. They simplify communication throughout disparate environments, making them ultimate for hybrid cloud and multi-cloud methods that demand interoperability.
- Allows asynchronous workflows: Brokers enable producers to ship messages and transfer on with out ready for shoppers to reply. This reduces system latency, improves responsiveness, and helps non-blocking operations crucial for real-time and high-availability programs.
With knowledge change, message brokers enable for selective scheduling for major duties between software program functions and permit dev groups to determine glitches sooner.
How does a message dealer work?
Consider a message dealer as a site visitors controller in your knowledge. As an alternative of providers speaking immediately to 1 one other and risking delays or downtime, it steps in to handle the circulation, making certain all the things will get to the correct place on the proper time.
1. Synchronous vs. asynchronous messaging
In a synchronous setup, one service sends a message to a different and waits for a response earlier than transferring ahead, a mannequin that creates tight coupling and delays if the receiving service is gradual or unavailable. This may be limiting in complicated programs the place providers must function independently.
Message brokers resolve this by enabling asynchronous communication. As an alternative of ready for a response, the producer sends the message to the dealer and strikes on. The buyer processes it later when it turns into out there. This enables for extra environment friendly multitasking and reduces system downtime throughout service interruptions.
2. From sender to receiver: inside dealer circulation
A producer generates a message and sends it to the message dealer. The dealer acts as an middleman that receives, shops, and forwards the message to the suitable client(s). Relying on how the dealer is configured, this workflow helps each one-to-one (point-to-point) and one-to-many (publish/subscribe) patterns.
As soon as a message reaches the dealer, it might be routed based mostly on logic like subject filters, routing keys, or exchanges. If the patron isn’t prepared or out there, the message may be saved briefly in a message queue, making certain it isn’t misplaced and is processed in the correct order as soon as the patron is again on-line..
Key capabilities dealt with by the message dealer:
Message brokers deal with a number of behind-the-scenes duties that simplify service integration. These embrace:
- Message marshaling and serialization: Changing messages into a regular format.
- Routing logic: Figuring out the place messages ought to go.
- Persistence and queuing: Quickly storing messages for reliability.
- Acknowledgments and retries: Managing supply affirmation and redelivery in case of failure.
3. Protocols and system decoupling
Consider it like talking totally different languages. Brokers act as interpreters, ensuring providers in-built Python or Java or working in several clouds nonetheless perceive each other.
This interplay mannequin decouples providers from one another; they not must know when or how different providers course of messages.
This decoupling simplifies deployments, improves resilience, and permits groups to independently scale or preserve providers with out risking downstream failures. For organizations transferring towards cloud-native, serverless, or microservices-based infrastructures, this sort of versatile communication mannequin is foundational.
Listed below are some basic parts of a message dealer:
- A producer is an app liable for transmitting messages. It is linked to the message dealer, also referred to as a writer, within the publish/subscribe mannequin.
- A client is a service that receives messages ready within the message dealer. They’re generally known as subscribers within the publish-subscribe sample.
- A queue or subject is a folder in a system. Message brokers use them to retailer messages.
- An change is a logical routing part that directs how messages are delivered to queues..
In apply, this structure helps a variety of use instances, from transactional workflows to event-driven pipelines, whereas making certain that knowledge is delivered reliably, solely as soon as, and in the correct order.
By offloading the heavy lifting of message coordination, brokers allow scalable, fault-tolerant programs that may evolve independently and carry out underneath strain.
What are the varieties of message dealer fashions?
Message brokers assist a number of messaging fashions that decide how messages are delivered and processed between producers and shoppers. The selection of mannequin impacts scalability, supply ensures, and the way providers work together.
Totally different workloads name for various messaging kinds. Let’s break down the three fashions you’re probably to come across, and when to make use of every:
1. Level-to-Level messaging mannequin
Within the P2P mannequin, a producer sends a message to a queue, and a single client retrieves it, making certain the message is processed solely as soon as. This mannequin is ultimate for duties that should not be repeated, like billing, payroll, or background jobs.
Instruments like Amazon SQS, RabbitMQ, and Apache ActiveMQ assist this mannequin with options corresponding to acknowledgments, retries, and dead-letter queues to make sure dependable, loss-free supply.

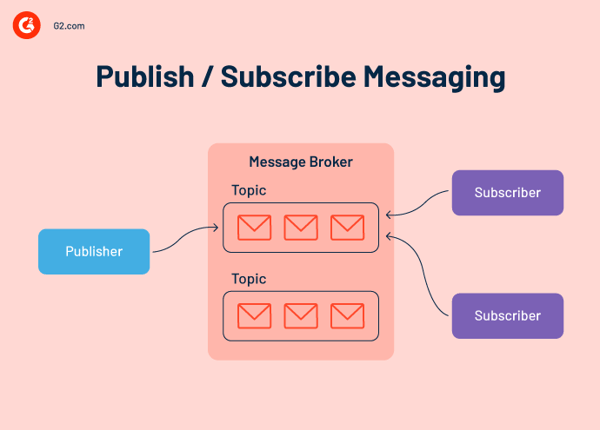
2. Publish/Subscribe messaging mannequin
The Pub/Sub mannequin follows a one-to-many sample: producers ship messages to a subject, and all subscribed shoppers obtain them concurrently. This mannequin is good for real-time occasion distribution throughout providers.
Use instances embrace notifying stock, delivery, and analytics programs after an “order positioned” occasion. Instruments like Apache Kafka, Amazon SNS, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub are constructed to assist this mannequin at scale.
3. Hybrid messaging mannequin
Hybrid brokers assist each one-to-one (P2P) and one-to-many (Pub/Sub) patterns in a single system, providing versatile routing based mostly on use case.
As an illustration, a logistics app would possibly use P2P to dispatch a trip whereas utilizing Pub/Sub to alert companions of site visitors modifications. Instruments like RabbitMQ, Redis Streams, and Kafka allow hybrid supply through routing guidelines, exchanges, or client teams.
These fashions kind the spine of recent messaging structure, balancing precision, scale, and pace in distributed programs.
Choosing the proper message dealer: framework & guidelines
With so many message dealer instruments out there, every optimized for various messaging patterns, throughput wants, and deployment fashions, it’s essential to guage your system necessities earlier than committing to 1. The appropriate selection relies upon not solely on efficiency benchmarks but additionally on operational tradeoffs, workforce experience, and structure match.
Listed below are the important thing components to think about when selecting a message dealer:
- Assess your message throughput and latency wants: In case your system ingests a excessive quantity of real-time knowledge, corresponding to logs, person conduct occasions, or IoT alerts, you may want a dealer constructed for efficiency at scale. Distributed streaming platforms like Apache Kafka or Redpanda are ultimate right here, able to dealing with tens of millions of messages per second with low-latency pipelines and chronic storage.
- Decide your supply ensures: Do your workloads require message supply at most as soon as, no less than as soon as, or precisely as soon as? For monetary transactions, order administration, or occasion sourcing, exactly-once semantics are important. Instruments like Kafka (with idempotent producers) or RabbitMQ (with acknowledgments and dead-letter queues) supply stronger supply controls than easier pub/sub programs.
- Match messaging fashions to your use case: Level-to-point programs are finest for job queues, whereas publish/subscribe works for occasions that have to be broadcast to a number of shoppers. Hybrid brokers like RabbitMQ or Apache Pulsar enable versatile routing guidelines to assist each one-to-one and one-to-many situations throughout the identical system.
- Contemplate language and protocol assist: In case you’re working in a polyglot atmosphere, say, Python microservices speaking to Java legacy programs, make sure the dealer helps interoperable protocols like AMQP, MQTT, or STOMP. RabbitMQ and ActiveMQ supply in depth cross-language assist, whereas Redis Streams and Kafka might require extra customized integration in sure stacks.
- Resolve between managed and self-hosted: Managed brokers like Amazon SQS/SNS or Google Pub/Sub supply quick provisioning, scaling, and monitoring with minimal setup. They’re ultimate for groups that need simplicity over management. Self-hosted choices like Kafka and RabbitMQ enable fine-tuned efficiency and customized routing however include greater upkeep overhead.
- Consider persistence and replay capabilities: Some use instances, like debugging workflows, rebuilding state, or making certain audit trails, require brokers that may retailer and replay messages. Kafka excels right here with its long-term log storage and message retention options, whereas ephemeral brokers like Redis could also be much less appropriate except knowledge loss is suitable.
- Align with already current infrastructure and stack: In case your workforce is already utilizing Redis for caching or Google Cloud for internet hosting, instruments like Redis Streams or Google Pub/Sub might supply higher integration and quicker time to manufacturing. Kubernetes-native instruments like NATS or Knative Eventing are additionally sturdy choices for containerized environments needing cloud-native message routing.
Selecting a dealer is not only about uncooked efficiency. It’s about discovering the correct device in your messaging patterns, workforce workflow, and development path.
Whether or not you’re constructing for high-throughput analytics or tightly managed transactional programs, aligning your selection with technical or enterprise objectives is essential to long-term messaging success.
Rising developments in message brokers (2025 and past)
- Serverless brokers: Instruments like AWS EventBridge and Google Eventarc allow message routing with out provisioning infrastructure, making them ultimate for event-driven, cloud-native apps.
- AI-powered brokers: New brokers are utilizing AI for good routing, message prioritization, and anomaly detection, lowering latency and bettering supply with out guide tuning
- Cloud-native messaging: Platforms like Apache Pulsar and NATS JetStream are constructed for Kubernetes, providing elastic scaling, stateless routing, and deep observability assist.
- Edge and IoT-focused brokers: Light-weight brokers like EMQX and Mosquitto assist offline-first supply and native queueing, constructed for sensors, units, and edge environments.
- Brokerless and decentralized messaging fashions: Peer-to-peer and distributed ledger–based mostly messaging is rising for zero-trust and Web3 environments, although nonetheless area of interest in adoption.
- Compliance-first and zero-trust messaging: Fashionable brokers are including options like encrypted payloads, audit trails, and coverage routing to satisfy rising knowledge governance and regulatory wants.
The message dealer of 2025 is not simply middleware; it’s a dynamic, context-aware communication layer woven into the infrastructure material. From serverless workloads to AI-driven routing, these developments level towards smarter, leaner, and safer messaging options throughout cloud and edge.
What are examples of message dealer instruments?
There’s no one-size-fits-all message dealer. Some excel in low-latency queues, others in occasion streaming or cloud-native scalability. Here is a snapshot of essentially the most extensively used instruments within the message dealer ecosystem:
Listed below are a few of their predominant traits:
- RabbitMQ is an open-source message dealer constructed on AMQP, recognized for versatile routing through direct, subject, and fanout exchanges. It helps each queue-based and pub/sub patterns and is right for transactional enterprise messaging.
- Amazon MQ is a cloud-based message dealer and part of Amazon Internet Providers (AWS). It provisions and maintains a message dealer for companies and reduces their routine duties.
- Apache Kafka is a distributed occasion streaming platform constructed for high-throughput, real-time knowledge pipelines. It excels in retaining and replaying message logs, making it ultimate for analytics, observability, and large-scale event-driven programs.
- Redis Streams provides light-weight message queue capabilities to Redis, delivering ultra-low-latency efficiency. It is an incredible match for real-time apps the place sturdiness is much less crucial, like stay chats or in-memory notifications.
- Amazon SNS presents push-based pub/sub messaging. It’s ultimate for broadcasting alerts, emails, or Lambda-triggered workflows, and sometimes enhances SQS in hybrid cloud patterns.
- Amazon Easy Queue Service (SQS) is a managed, pull-based queueing service that scales robotically. With built-in integration throughout the AWS ecosystem, it’s generally utilized in serverless and microservices architectures.
- Google Cloud Pub/Sub permits world, real-time pub/sub messaging. It’s optimized for high-scale, low-latency pipelines throughout cloud-native apps and knowledge streaming platforms.
- Azure Service Bus is Microsoft’s enterprise-grade messaging service with assist for dead-letter queues, message classes, and duplicate detection — typically utilized in. NET-heavy environments.
These instruments are adept at dealing with complicated messaging logic, storing technical documentation, and performing as an middleman between the app and the developer.
Energy your structure with the correct message dealer
From real-time occasion streaming to sturdy message queues, the correct dealer could make or break your system’s efficiency. G2 presents trusted evaluations and side-by-side comparisons that can assist you select the very best match in your messaging wants.
Evaluate prime message queue and occasion streaming instruments on G2 now.
Message brokers vs. occasion streaming platforms
Whereas each message brokers and occasion streaming platforms deal with inter-service communication, they serve distinct functions and excel in several architectural situations.
.png?width=600&name=Message%20brokers%20vs.%20event%20streaming%20platforms%20(2).png)
Message brokers are designed to reliably route messages between producers and shoppers, typically utilizing queue-based or pub/sub fashions. They’re ultimate for transactional workflows, asynchronous activity processing, and decoupling providers in microservices or hybrid cloud environments. Brokers like RabbitMQ, Amazon SQS, and ActiveMQ concentrate on message sturdiness, supply ensures, and assist for a number of protocols, making them nice to be used instances the place reliability and interoperability matter most.
Occasion streaming platforms, like Apache Kafka or Redpanda, concentrate on ingesting and processing excessive volumes of time-ordered occasion knowledge in actual time. Quite than discarding messages after supply, they persist them for a configurable interval, permitting for replay, audit, and batch processing. These platforms are constructed for knowledge pipelines, real-time analytics, and stream processing, the place scale, throughput, and long-term storage of occasion logs take precedence over supply ensures.
In brief: use message brokers when communication reliability is crucial; select occasion streaming when real-time knowledge circulation and processing are the precedence.
Message dealer vs. enterprise service bus vs. API
Fashionable architectures typically depend on varied integration patterns to attach programs, providers, and functions.
Whereas message brokers, enterprise service buses (ESBs), and APIs all serve this objective, they differ considerably in how they deal with communication, scalability, and system decoupling.
| Characteristic | Message Dealer | Enterprise Service Bus | API |
| Major Goal | Decouples providers by async message routing | Centralized integration and orchestration of a number of providers | Direct, synchronous communication between providers |
| Communication Model | Asynchronous (queue or pub/sub based mostly) | Synchronous and asynchronous | Sometimes synchronous (REST/HTTP), generally async (Webhooks, GraphQL Subscriptions) |
| Protocol assist | AMQP, MQTT, STOMP, proprietary | XML, SOAP, HTTP, FTP, JMS, SMTP | HTTP/HTTPS, REST, gRPC, WebSocket |
| Routing Logic | Easy to complicated routing through queues, matters, or exchanges | Superior orchestration and mediation logic | No built-in routing, outlined manually in consumer/server logic |
| Complexity | Light-weight and simple to arrange | Advanced, heavy, and more durable to scale | Light-weight to average, relying on implementation |
| Scalability | Excessive, suited to distributed and microservices architectures | Decrease, more durable to scale and debug | Is dependent upon implementation, can scale through load balancers or API gateways |
| Resilience / Decoupling | Excessive, decouples producers and shoppers | A medium, centralized bus can develop into a bottleneck | Low — tight coupling between providers except decoupled through queues or occasions |
| Splendid Use Circumstances | Microservices, async workflows, background processing | Legacy programs, service orchestration, complicated B2B integrations | Request-response providers, third-party integration, frontend-backend calls |
| Examples | RabbitMQ, Kafka, Amazon SQS/SNS, ActiveMQ | MuleSoft, IBM Integration Bus, TIBCO ESB | REST APIs, GraphQL, OpenAPI, Postman-exposed endpoints |
Every method has its place relying in your structure. Choosing the proper integration methodology comes right down to your system’s complexity, efficiency wants, and the way tightly or loosely you need your providers coupled.
What are the advantages of a message dealer?
Message brokers play a central position in constructing scalable, resilient, and decoupled programs. Under are the core advantages they provide, not solely from a technical standpoint, but additionally by way of enterprise affect and long-term architectural flexibility.
- Allows asynchronous communication: Message brokers decouple providers by permitting producers and shoppers to function independently. As an alternative of ready for real-time responses, providers publish and eat messages as wanted. This improves system responsiveness and makes distributed architectures extra fault-tolerant, particularly when coping with latency or variable workloads.
- Improves system efficiency and scanability: Brokers stop front-end delays by offloading background duties like e-mail sends, file uploads, or billing. Messages are queued and processed behind the scenes, enabling elastic scaling of providers. This results in quicker person experiences and environment friendly infrastructure utilization, particularly throughout excessive site visitors.
- Guarantee dependable message supply: Message brokers present supply ensures by retries, acknowledgments, and dead-letter queues. If a client fails, the message isn’t misplaced; it’s retried or quarantined for overview. This resilience is crucial in sectors like finance or logistics, the place each message have to be accounted for.
- Simplifies service decoupling and upkeep: With a dealer within the center, providers may be up to date, scaled, or restarted with out impacting the remainder of the system. This decoupling permits unbiased deployments, quicker iteration, and decrease threat of cascading failures, which is right for agile groups managing microservices or modular platforms.
- Enhances observability and restoration: Many brokers supply built-in integration with monitoring and observability instruments. Groups acquire visibility into message circulation, latency, and queue well being. This traceability helps quicker debugging, proactive efficiency tuning, and more practical incident response throughout distributed environments.
Whether or not you are scaling microservices or modernizing legacy workflows, message brokers present the spine for resilient, future-ready architectures.
What are the challenges of a message dealer?
One notable disadvantage of message brokers is the problem of initiating and managing asynchronous operations that customers won’t have experience in. Let’s take a look at different drawbacks of implementing a message dealer for knowledge:
- Elevated system complexity: Integrating a message dealer into your system provides a brand new part to the general infrastructure. This requires addressing further components, corresponding to supporting the community between components or safety dangers. Message brokers may result in system inconsistencies as some components might not have present knowledge till the messages are transmitted and interpreted.
- Debugging may be cumbersome: Suppose you’re taking a number of steps to deal with a single request through the message dealer. You submitted a message however didn’t obtain a response. Figuring out the error supply may be difficult as a result of every service has its personal logs. Subsequently, it’s good to supply message-tracing options when creating programs that use message brokers.
- Steeper studying curve: Message brokers require many setup and configuration choices and are not as simple to implement. Queue and message sizes, queue conduct, supply parameters, and message time-to-live (TTL) are just some variables that customers can select from.
Whereas message brokers assist handle complicated messaging logic, an incorrect deployment could cause unwarranted system crashes or expose your crucial knowledge.
What are the highest use instances of message brokers?
Message brokers are important for orchestrating dependable, asynchronous communication throughout distributed programs.
From fintech to cloud-native environments, they permit scalable, decoupled workflows that enhance fault tolerance and real-time responsiveness.
- Fee processing and monetary programs: Guarantee exactly-once message supply for delicate operations like fund transfers, fee approvals, and fraud checks. Brokers like Kafka and RabbitMQ stop duplication and assist real-time audit trails.
- E-commerce order administration: Energy checkout, stock updates, and success notifications with out risking order loss. Pub/sub brokers like Amazon SNS decouple programs to maintain providers responsive even throughout site visitors spikes.
- Cloud-native eventing and serverless apps: Instruments like AWS EventBridge or Google Pub/Sub enable cloud apps to set off capabilities, workflows, or providers based mostly on occasions, with out direct dependencies or infrastructure overhead.
- Microservices orchestration: Brokers assist particular person providers talk asynchronously, enabling groups to deploy, scale, and handle parts independently. They are perfect for distributed programs utilizing Kubernetes or service meshes.
- Safe knowledge transmission in regulated industries: Use brokers with encryption, entry management, and audit logging to securely transfer knowledge in sectors like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI), or authorities (FedRAMP).
These use instances present that message brokers aren’t simply middleware; they’re foundational to constructing quick, versatile, and future-ready programs.
Message brokers: often requested questions (FAQs)
1. When ought to I take advantage of a message dealer as a substitute of REST APIs?
Use a message dealer when your structure requires asynchronous processing, offline tolerance, or event-based communication. Not like REST APIs, brokers assist decouple providers and enhance resilience, particularly in microservices and hybrid cloud setups.
2. RabbitMQ vs Kafka: Which is healthier for microservices?
RabbitMQ is finest for low-latency, transactional messaging between tightly scoped providers. Kafka is healthier suited to large-scale, event-driven microservices that want persistent log storage and message replay capabilities.
3. What’s the very best message dealer for serverless functions?
Cloud-native brokers like Amazon SQS, SNS, and EventBridge combine seamlessly with serverless platforms like AWS Lambda, enabling scalable, event-driven programs with out guide queue administration.
4. What’s the distinction between pub/sub and message queuing fashions?
Pub/sub delivers messages to all subscribers in actual time, making it ultimate for broadcasting occasions. Queuing sends every message to a single client, which works properly for activity distribution and background job execution.
5. Ought to I select a managed message dealer or a self-hosted one?
Managed brokers like Amazon MQ, Google Pub/Sub, and Azure Service Bus cut back infrastructure overhead and auto-scale with demand. Self-hosted choices like Kafka or RabbitMQ supply deeper management however require extra DevOps effort.
6. How do I select the correct message dealer for my tech stack?
Have a look at throughput, latency, supply ensures, protocol assist, and ecosystem compatibility. Use comparability platforms like G2 to filter instruments that suit your structure — whether or not it’s serverless, Kubernetes-native, or monolithic.
Construct smoother async bridges of knowledge
With a message dealer, you may produce a stable and scalable producer-consumer structure. It permits builders to automate the success lifecycle and change readable messages to make sure the general clean functioning of the infrastructure.
Message brokers have gotten more and more essential as companies revamp their programs in anticipation of the cloud. Merely put, message brokers are important for contemporary, technologically creating societies.
Monitor your ad-hoc software program integrations with the very best stream analytics software program and monitor efficiency benchmarks and thresholds with ease.
This text was initially written in 2024. It has been up to date with new data.

